Beetroot
Overview
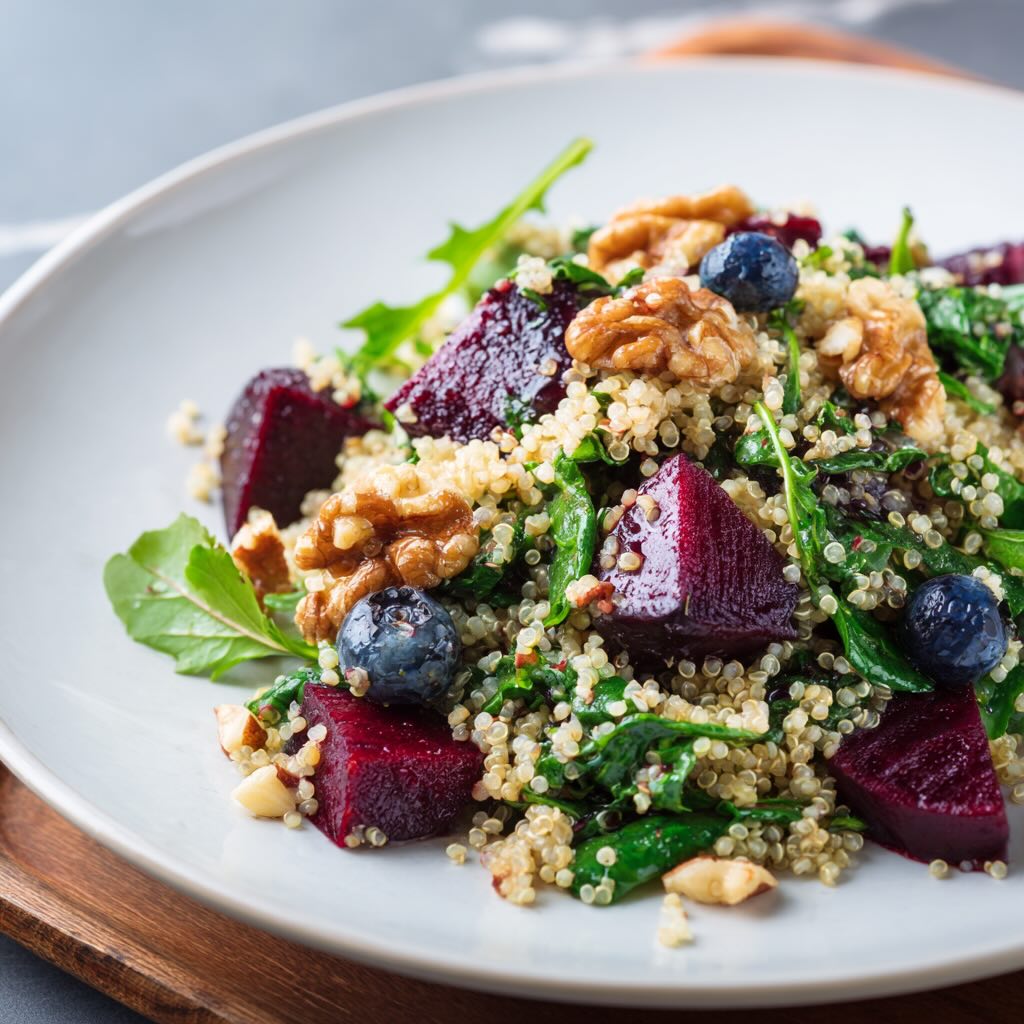
Beetroot provides dietary nitrates that convert to nitric oxide, supporting vascular function and mitochondrial efficiency. Rich in betalains (antioxidant pigments), folate, and minerals, beetroot contributes to cardiovascular health and metabolic resilience.
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Raw or lightly cooked preserves nitrate content; roasting enhances flavor while maintaining nutritional value
- Nitrate conversion to nitric oxide is enhanced by oral bacteria; consuming with leafy greens can support this pathway
- Part of nitrate-rich vegetable intake supporting vascular and mitochondrial function
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hormonal Response | Magnesium | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports calcium modulation along with vitamin D, taurine, phospholipids, and flavonoids; supports insulin sensitivity, sympathetic arousal, and mitochondrial excitability | |
| Insulin Response | Magnesium | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism; magnesium deficiency is associated with insulin resistance; supports enzymes involved in glucose metabolism | |
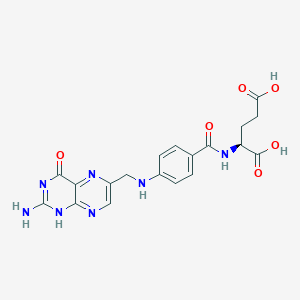
| Methylation | Vitamin B9 (Folate; 5-MTHF) | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential cofactor in remethylation of homocysteine to methionine, which is converted to S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe); SAMe fuels synthesis of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin and drives phospholipid methylation in neuronal membranes | |
| Mitochondrial Support | Iron | Contextual / minor contributor | Critical for oxygen delivery to the brain via hemoglobin; supports mitochondrial function and energy production | |
| Mitochondrial Support | Magnesium | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports enzymes involved in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle (processes that generate ATP from glucose); binds to ATP and all triphosphates in cells to activate them | |
| Mitochondrial Support | Manganese | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports mitochondrial antioxidant defense through MnSOD activity | |
| Mitochondrial Support | Nitrate | Contextual / minor contributor | Dietary nitrates convert to nitric oxide (NO), which supports vascular function and cerebral blood flow, enhancing oxygen and nutrient delivery to brain tissue; nitric oxide improves mitochondrial efficiency by optimizing blood flow and supporting vascular tone | |
| Neurochemical Balance | Iron | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential cofactor for tyrosine hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in the conversion of tyrosine to dopamine; critical for catecholamine synthesis | |
| Neurochemical Balance | Magnesium | Contextual / minor contributor | Broad cofactor for neurotransmitter synthesis and receptor modulation (e.g., NMDA, GABA); functions as an NMDA receptor antagonist and GABA receptor modulator; assists enzymes involved in synthesis of dopamine and serotonin | |
| Neurochemical Balance | Potassium | Contextual / minor contributor | Critical for membrane potential, nerve signaling, and neuronal excitability; adequate intake balances sodium effects | |
| Neurochemical Balance | Vitamin B9 (Folate; 5-MTHF) | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports neurotransmitter synthesis through methylation; cofactor for dopamine synthesis alongside iron, B6, and omega-3s | |
| Oxidative Stress | Manganese | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential cofactor for MnSOD (SOD2), supporting detoxification of superoxide within the mitochondrial matrix | |
| Stress Response | Magnesium | Contextual / minor contributor | Helps manage stress responses; combined with vitamin D reduced behavioral problems; synergy with zinc and omega-3s reported |
References
- Dietary nitrates from beetroot and leafy greens convert to nitric oxide, supporting vascular function and mitochondrial efficiency
- Betalains in beetroot provide antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties