Sauerkraut
Overview
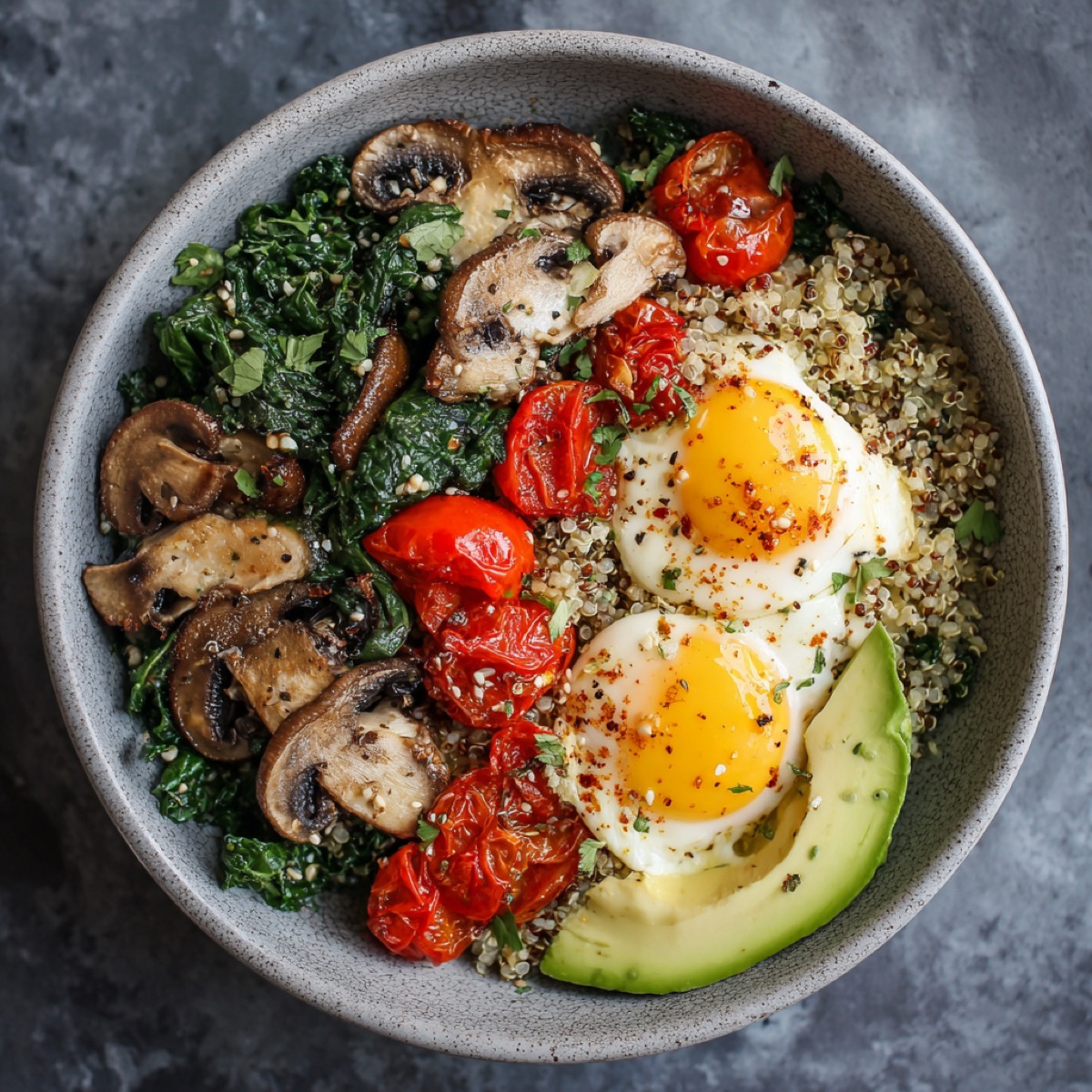
Sauerkraut is fermented cabbage providing live Lactobacillus probiotics, postbiotic compounds, and enhanced nutrient bioavailability. Fermented foods such as sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir, miso, and kombucha provide live microbes + postbiotic peptides; improved SCFA pools; vagal signaling.
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Choose unpasteurized for live probiotics
- Regular but not excessive intake
- Part of fermented foods rotation
- Supports gut microbiome diversity
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gut–Brain Axis & Enteric Nervous System (ENS) | Acetate | Contextual / minor contributor | Byproduct of fibre fermentation; supports intestinal barrier integrity; regulates immune responses; promotes synthesis of key neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin | |
| Gut–Brain Axis & Enteric Nervous System (ENS) | Propionate | Contextual / minor contributor | Byproduct of fibre fermentation; supports intestinal barrier integrity; regulates immune responses | |
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Acetate | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports immune regulation and anti-inflammatory processes | |
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Propionate | Contextual / minor contributor | Helps reduce neuroinflammation and protects the blood-brain barrier; enhances cognitive function | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Propionate | Contextual / minor contributor | Stimulates secretion of norepinephrine and may influence dopamine regulation; promotes synthesis of key neurotransmitters |
References
- Fermented Foods: Sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir, miso, kombucha - Live microbes + postbiotic peptides; improved SCFA pools; vagal signaling
- Sauerkraut: Fermented cabbage, rich in Lactobacillus