Egg Yolks
Overview
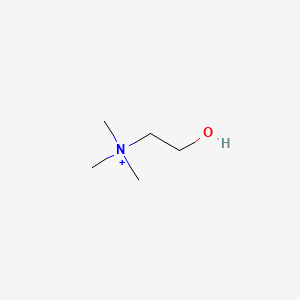
Egg yolks provide choline (acetylcholine precursor), lutein/zeaxanthin (carotenoids), and fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K2), supporting neurotransmitter synthesis and brain health. Acetylcholine and choline food sources include egg yolks, fish roe, soy, wheat germ, and liver.
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Choose pasture-raised for higher nutrient content
- Gentle cooking preserves nutrients
- Important for choline and carotenoid intake
- Pair with carotenoid-rich vegetables for enhanced absorption
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gut–Brain Axis & Enteric Nervous System (ENS) | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Choline is metabolised by gut bacteria; some strains (e.g. Lactobacillus) can produce acetylcholine. Microbial choline metabolism (e.g. trimethylamine) shows inter-individual variability and may influence host metabolism and gut–brain signalling. | |
| Gut–Brain Axis & Enteric Nervous System (ENS) | Vitamin D | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports gut barrier integrity; nutrient deficiencies including vitamin D disrupt tight junctions, increasing permeability | |
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Choline-derived betaine supports homocysteine remethylation; elevated homocysteine is linked to oxidative stress and inflammatory signalling. Phosphatidylcholine supports membrane integrity and cell signalling in immune and redox contexts. | |
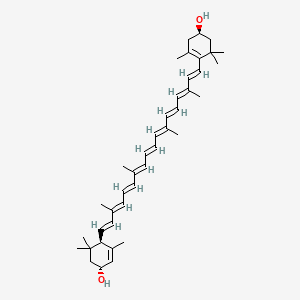
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Lutein | Contextual / minor contributor | Anti-inflammatory properties; supports immune regulation | |
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Zeaxanthin | Contextual / minor contributor | Anti-inflammatory properties; supports immune regulation | |
| Metabolic & Neuroendocrine Stress (HPA Axis & ANS) | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Choline supports hepatic VLDL assembly and lipid export; methyl donors (choline, betaine) may influence adenosine metabolism and HPA axis activity. Adequate choline status supports metabolic stability and stress physiology. | |
| Metabolic & Neuroendocrine Stress (HPA Axis & ANS) | Vitamin D | Contextual / minor contributor | Modulates immune responses to reduce inflammation in the brain; supports stress response through neurotrophic and immune effects | |
| Methylation & One-Carbon Metabolism | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Precursor to trimethylglycine (TMG/betaine), a dietary methyl donor that helps recycle homocysteine to methionine via an alternative pathway; supports one-carbon metabolism alongside folate, riboflavin, and B12; influences methylation dynamics relevant to MTHFR and COMT activity | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Phosphatidylcholine and other choline-containing phospholipids support mitochondrial membrane integrity and energy metabolism; choline-derived betaine contributes to one-carbon status that can influence mitochondrial resilience | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential precursor for acetylcholine synthesis, supporting memory, learning, and neuroplasticity; supports membrane phospholipid biosynthesis (PC) which is critical for membrane fluidity and neurotransmitter receptor function; phospholipid methylation (PLM) alters membrane structure, facilitating faster neuronal recovery and influencing ion channel behavior in gamma oscillations linked to attention and cognition |
References
- Acetylcholine and choline: Egg yolks, fish roe, soy, wheat germ, liver
- Carotenoids are abundant in leafy greens, orange and yellow vegetables, corn, and egg yolks
- Pasture-raised egg yolks for nutrient density