Olive Oil (Early Harvest)
Overview
Early harvest extra virgin olive oil is a precision food in the BRAIN Diet, harvested from olives picked earlier in the season when they contain significantly higher concentrations of bioactive compounds. Olive oil's brain benefits come from polyphenols, not fatty acids. Early harvest oils have substantially higher levels of the key secoiridoids and phenolics that provide brain health benefits:
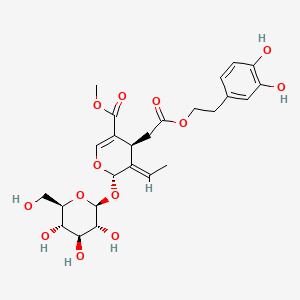
- Oleuropein aglycone → mitophagy, SIRT1, AMPK activation (up to 53-56% more CoQ10 than later harvest)
- Oleocanthal → NF-κB inhibition, anti-inflammatory effects
- Oleacein → antioxidant, NRF2 activation
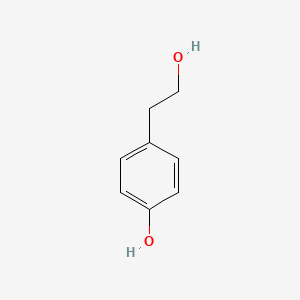
- Tyrosol / Hydroxytyrosol → neuroprotective effects
These enhanced bioactive levels support mitochondrial function, antioxidant networks, and anti-inflammatory pathways, making early harvest olive oil a valuable component of precision dietary strategies for brain health. The implementation of the BRAIN diet must go beyond a standard nutrient density focus; it's about choosing foods for their specific bioactive potential: early harvest extra virgin olive oil with higher levels of CoQ10, oleuropein, oleocanthal, oleacein, hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, and total polyphenols.
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Best used for salad dressings, drizzling, and low-heat applications to preserve polyphenols and CoQ10
- Avoid high-heat cooking to prevent degradation of bioactive compounds
- Store away from heat and light to preserve antioxidant properties and CoQ10 levels
- Look for harvest date information on labels; early harvest typically occurs in September-October (Northern Hemisphere)
- Total CoQ dropped by 53%-56% between three weeks of the harvesting of two brands, highlighting the critical importance of harvest timing
- Higher polyphenol content provides stronger antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects compared to standard EVOO
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Hydroxytyrosol (Olive Polyphenol) | Contextual / minor contributor | Strong anti-inflammatory profile; contributes to neuroprotective effects of extra-virgin olive oil | |
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Oleocanthal | Contextual / minor contributor | NF-κB inhibition; strong anti-inflammatory effects similar to ibuprofen; contributes to neuroprotective effects of extra-virgin olive oil | |
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Oleuropein | Contextual / minor contributor | Anti-inflammatory properties; contributes to neuroprotective effects of extra-virgin olive oil | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Oleuropein | Contextual / minor contributor | Oleuropein aglycone (the active form) supports mitophagy, SIRT1 activation, and AMPK activation; enhances mitochondrial function, autophagy, and neuroprotective effects through modulation of mitochondrial dynamics and antioxidant pathways | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Tyrosol | Contextual / minor contributor | Neuroprotective effects; contributes to brain health benefits of extra-virgin olive oil |
References
- Olive oil's brain benefits come from polyphenols, not fatty acids. The bioactive power of early harvest EVOO is from secoiridoids and phenolics: oleuropein aglycone (mitophagy, SIRT1, AMPK), oleocanthal (NF-κB inhibition), oleacein (antioxidant, NRF2 activation), and tyrosol/hydroxytyrosol (neuroprotective effects)
- Early harvest extra virgin olive oil with higher levels of CoQ10, oleuropein, oleocanthal, oleacein, hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, and total polyphenols Gasmi et al. 2022
- Total CoQ dropped by 53%-56% between three weeks of the harvesting of two brands, highlighting variation by producer and harvest time
- The implementation of the BRAIN diet must go beyond a standard nutrient density focus, it's about choosing foods for their specific bioactive potential: early harvest extra virgin olive oil with higher levels of CoQ10, oleuropein, oleocanthal, oleacein, hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, and polyphenols
- Early harvest oils have substantially higher bioactive content (CoQ10, oleuropein, oleocanthal, oleacein, hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, polyphenols) compared to standard EVOO
- Olive oil phenolic compounds, particularly oleuropein aglycone, oleocanthal, oleacein, and hydroxytyrosol, support mitochondrial function, autophagy, and neuroprotective effects through modulation of mitochondrial dynamics, SIRT1, AMPK, NF-κB inhibition, and NRF2 activation