MCT Oil
Overview
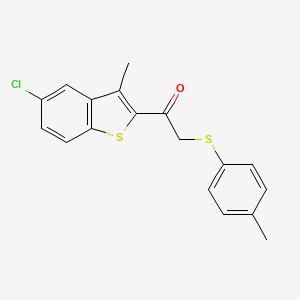
MCT oil is concentrated medium-chain triglycerides (C6, C8, C10) providing rapid energy for the brain and supporting ketone production. It contains caprylic triglyceride (C8), capric triglyceride (C10), and caproic triglyceride (C6). Coconut Oil / MCT Oil provides MCTs (C8, C10), rapid energy for brain, and supports ketone production.
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Use in smoothies or small portions
- Start with small amounts
- Supports ketone production
- Part of brain energy strategy
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Capric Triglyceride (Tridecanoin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Capric triglyceride (C10) is converted to ketones (beta-hydroxybutyrate) in the liver, which serve as an alternative energy substrate for mitochondria; ketones can be used by brain mitochondria when glucose metabolism is impaired, supporting ATP production and mitochondrial function | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Caproic Triglyceride (Tricaproin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Caproic triglyceride (C6) is converted to ketones (beta-hydroxybutyrate) in the liver, which serve as an alternative energy substrate for mitochondria; ketones can be used by brain mitochondria when glucose metabolism is impaired, supporting ATP production and mitochondrial function | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Caprylic Triglyceride (Trioctanoin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Caprylic triglyceride (C8) is converted to ketones (beta-hydroxybutyrate) in the liver, which serve as an alternative energy substrate for mitochondria; ketones can be used by brain mitochondria when glucose metabolism is impaired, supporting ATP production and mitochondrial function | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | MCT (Medium-Chain Triglycerides) | Contextual / minor contributor | MCTs are converted to ketones (beta-hydroxybutyrate) in the liver, which serve as an alternative energy substrate for mitochondria; ketones can be used by brain mitochondria when glucose metabolism is impaired, supporting ATP production and mitochondrial function | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Capric Triglyceride (Tridecanoin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Ketones produced from capric triglyceride provide ATP through mitochondrial metabolism; ATP is essential for neurotransmitter synthesis, release, and reuptake, indirectly supporting neurochemical balance by ensuring adequate energy for neuronal function | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Caproic Triglyceride (Tricaproin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Ketones produced from caproic triglyceride provide ATP through mitochondrial metabolism; ATP is essential for neurotransmitter synthesis, release, and reuptake, indirectly supporting neurochemical balance by ensuring adequate energy for neuronal function | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Caprylic Triglyceride (Trioctanoin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Ketones produced from caprylic triglyceride provide ATP through mitochondrial metabolism; ATP is essential for neurotransmitter synthesis, release, and reuptake, indirectly supporting neurochemical balance by ensuring adequate energy for neuronal function | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | MCT (Medium-Chain Triglycerides) | Contextual / minor contributor | Ketones produced from MCTs provide ATP through mitochondrial metabolism; ATP is essential for neurotransmitter synthesis, release, and reuptake, indirectly supporting neurochemical balance by ensuring adequate energy for neuronal function |
References
- Coconut Oil / MCT Oil: MCTs (C8, C10), rapid energy for brain, supports ketone production
- Antimicrobial Lipids: Medium-chain triglycerides (MCT oil, coconut oil), caprylic acid