Kefir
Overview
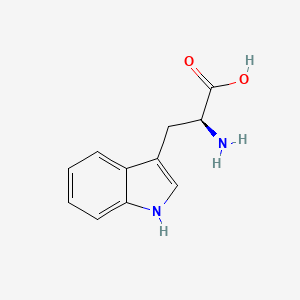
Kefir is fermented milk providing diverse probiotics, including potential GABA-producing strains, and postbiotic compounds. Fermented Foods: Sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir, miso, kombucha provide live microbes + postbiotic peptides; improved SCFA pools; vagal signaling. Kefir: Fermented milk drink, diverse probiotic strains. Levilactobacillus brevis is active in L. brevis strains isolated from fermented foods, such as kimchi, kefir, and pickles, and can produce GABA.
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Choose products with live active cultures for probiotic benefits
- Part of fermented foods rotation; fermented foods provide live microbes + postbiotic peptides; improved SCFA pools; vagal signaling
- Supports gut microbiome diversity; dietary diversity (≥30 plant foods per week) supports microbial richness and resilience
- Potential GABA production via specific strains; Levilactobacillus brevis strains isolated from fermented foods, such as kimchi, kefir, and pickles can produce GABA
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Calcium | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential for nerve impulse transmission and neurotransmission | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Tryptophan | Contextual / minor contributor | Precursor for serotonin and melatonin; brain entry competes at LAT1 with other large neutral amino acids (LNAAs); carbohydrate-rich, low-protein meals raise the plasma tryptophan:LNAA ratio because insulin pushes competing LNAAs out to muscles; can feed NAD+ synthesis via the kynurenine pathway | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Tyrosine | Contextual / minor contributor | Catecholamine precursor (dopamine, norepinephrine); brain transport via LAT1 competes with other LNAAs; iron is an essential cofactor for tyrosine hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in conversion of tyrosine to dopamine; cofactors include iron, B6, folate, omega-3s, and BH₄ (tetrahydrobiopterin) to support rate-limiting steps in catecholamine synthesis |
References
- Fermented Foods: Sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir, miso, kombucha - Live microbes + postbiotic peptides; improved SCFA pools; vagal signaling
- Kefir: Fermented milk drink, diverse probiotic strains
- Levilactobacillus brevis... This bacteria is active in L. brevis strains isolated from fermented foods, such as kimchi, kefir, and pickles
- Nutrient density is a central premise... kimchi and kefir give microbiome support
- GABA: Main inhibitory neurotransmitter; food sources include green tea, fermented foods, polyphenols (genistein), spinach, almonds, pumpkin seeds; Levilactobacillus brevis strains in kefir can produce GABA