Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Overview
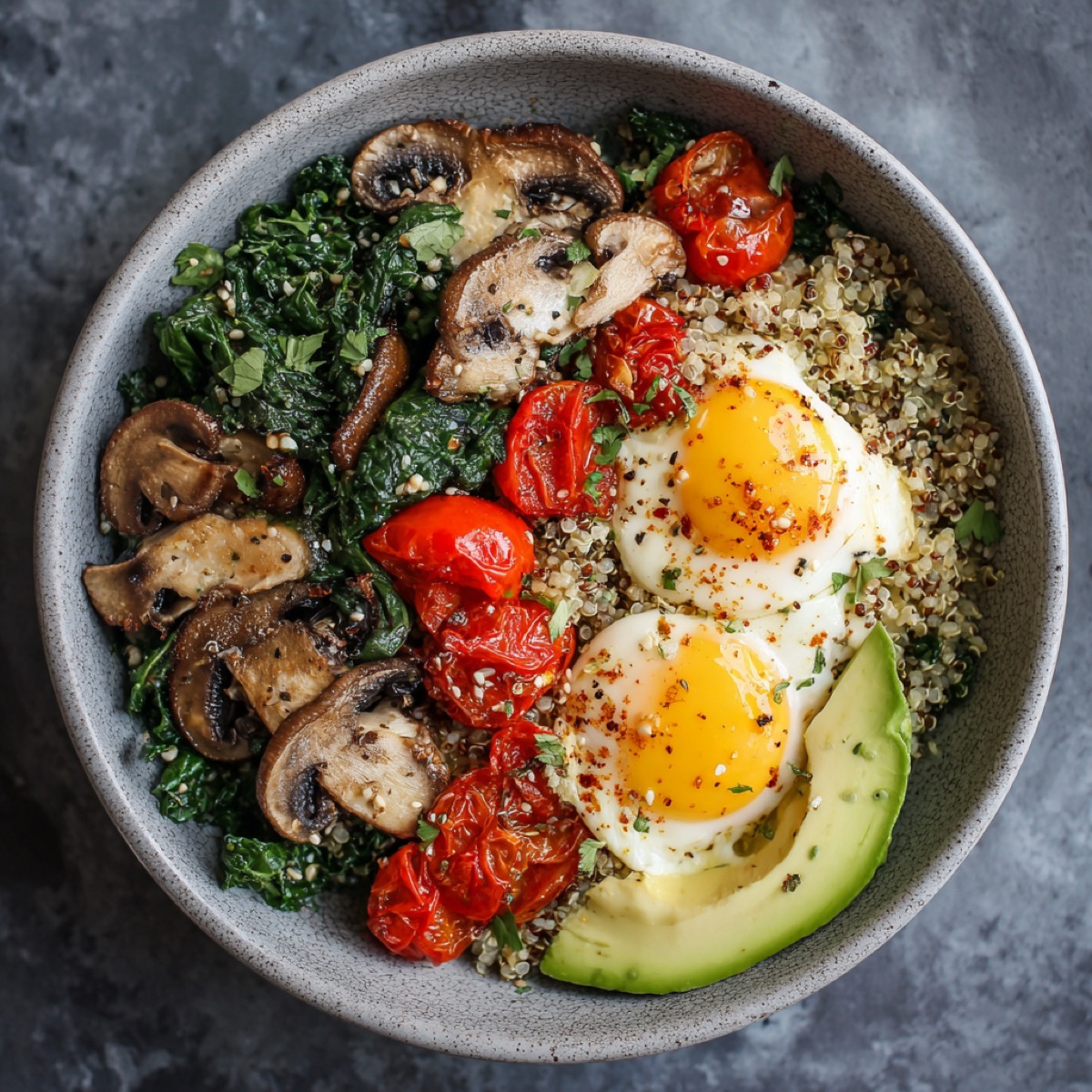
Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is a cornerstone fat in the BRAIN Diet. Importantly, olive oil's brain benefits come from polyphenols, not fatty acids. The bioactive power of EVOO is derived from secoiridoids and phenolics, including:
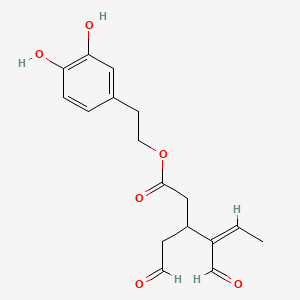
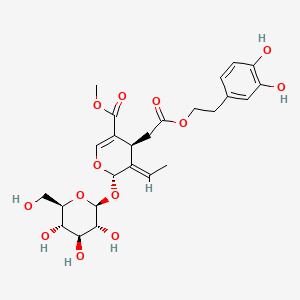
- Oleuropein aglycone → supports mitophagy, SIRT1 activation, and AMPK activation
- Oleocanthal → NF-κB inhibition, anti-inflammatory effects
- Oleacein → antioxidant, NRF2 activation
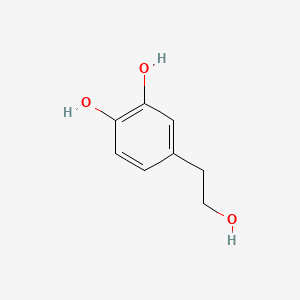
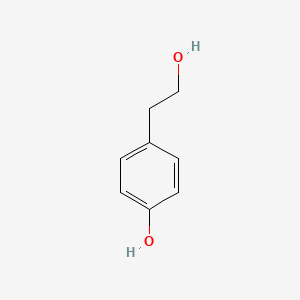
- Tyrosol / Hydroxytyrosol → neuroprotective effects
Early harvest extra virgin olive oil contains significantly higher concentrations of these bioactive compounds (oleuropein, oleocanthal, oleacein, hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol) compared to standard EVOO or regular olive oil. Early harvest oils may also contain CoQ10 in useful quantities, though standard EVOO typically does not. These enhanced polyphenol levels support mitochondrial function, antioxidant networks, and anti-inflammatory pathways, making early harvest olive oil a valuable component of precision dietary strategies for brain health.
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Best used for salad dressings, drizzling, low-heat cooking to preserve polyphenols
- Avoid high-heat cooking to preserve polyphenols and prevent oxidation
- Early harvest oils have higher bioactive content (oleuropein, polyphenols) and may contain CoQ10 in useful quantities
- Store away from heat and light to preserve antioxidant properties
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Hydroxytyrosol (Olive Polyphenol) | Contextual / minor contributor | Strong anti-inflammatory profile; contributes to neuroprotective effects of extra-virgin olive oil | |
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Oleocanthal | Contextual / minor contributor | NF-κB inhibition; strong anti-inflammatory effects similar to ibuprofen; contributes to neuroprotective effects of extra-virgin olive oil | |
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Oleuropein | Contextual / minor contributor | Anti-inflammatory properties; contributes to neuroprotective effects of extra-virgin olive oil | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Oleuropein | Contextual / minor contributor | Oleuropein aglycone (the active form) supports mitophagy, SIRT1 activation, and AMPK activation; enhances mitochondrial function, autophagy, and neuroprotective effects through modulation of mitochondrial dynamics and antioxidant pathways | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Tyrosol | Contextual / minor contributor | Neuroprotective effects; contributes to brain health benefits of extra-virgin olive oil |
References
- Olive oil's brain benefits come from polyphenols, not fatty acids. The bioactive power of EVOO is from secoiridoids and phenolics: oleuropein aglycone (mitophagy, SIRT1, AMPK), oleocanthal (NF-κB inhibition), oleacein (antioxidant, NRF2 activation), and tyrosol/hydroxytyrosol (neuroprotective effects)
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil: hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, oleuropein, oleocanthal, oleacein, squalene; strong antioxidant & anti-inflammatory profile
- Early harvest extra virgin olive oil with higher levels of oleuropein, oleocanthal, oleacein, hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, and total polyphenols; may contain CoQ10 in useful quantities
- Early harvest oils have substantially higher bioactive content (oleuropein, polyphenols) compared to standard EVOO
- Polyphenol sources including extra virgin olive oil support gut barrier integrity, TLR4 suppression, LPS neutralization, and microglial activation dampening