Oranges
Overview
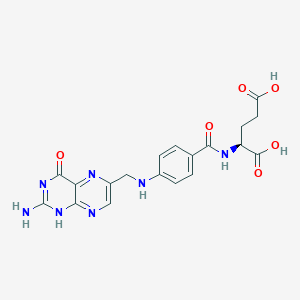
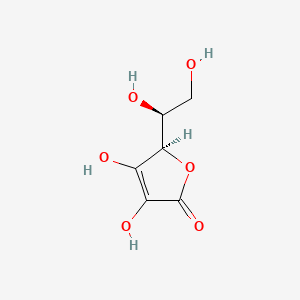
Oranges provide high vitamin C content that enhances non-heme iron absorption when paired with iron-rich plant foods. Pairing plant-based iron sources with citrus enhances iron absorption, and eating beans with vitamin C-rich foods (e.g., tomatoes, peppers, citrus) improves iron bioavailability.
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Pair with iron-rich plant meals to enhance absorption
- Can be consumed as whole fruit or juice (whole fruit preferred for fiber)
- Part of food synergy strategy
- Supports iron sufficiency in plant-based diets
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Vitamin C (Ascorbate) | Contextual / minor contributor | Antioxidant properties; supports anti-inflammatory effects | |
| Metabolic & Neuroendocrine Stress (HPA Axis & ANS) | Vitamin C (Ascorbate) | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports stress response through antioxidant and neurochemical effects | |
| Methylation & One-Carbon Metabolism | Vitamin B9 (Folate; 5-MTHF) | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential cofactor in remethylation of homocysteine to methionine, which is converted to S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe); SAMe fuels synthesis of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin and drives phospholipid methylation in neuronal membranes | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Vitamin B9 (Folate; 5-MTHF) | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports neurotransmitter synthesis through methylation; cofactor for dopamine synthesis alongside iron, B6, and omega-3s | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Vitamin C (Ascorbate) | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports norepinephrine synthesis; transported in brain via SVCT2 |
References
- Pairing plant-based iron sources with citrus (Hallberg et al. 1989) enhances iron absorption
- Eat your beans with vitamin C-rich foods (e.g., tomatoes, peppers, citrus)
- Norepinephrine: Same as dopamine sources + citrus, bell peppers (vitamin C)