Organ Meats
Overview
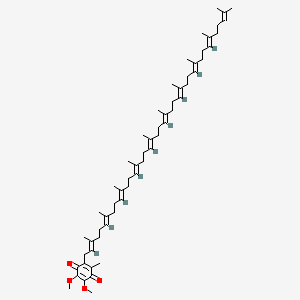
Organ meats (offal) are among the most nutrient-dense foods, providing high levels of B12, CoQ10, iron, and other brain-supportive nutrients. Organ meats (heart, liver), oily fish (sardines, mackerel), beef are top sources for CoQ10, and occasional offal consumption is recommended for nutrient density.
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Source from grass-fed/pasture-raised when possible
- Moderate consumption due to high nutrient density
- Important for closing nutrient gaps
- Part of nose-to-tail approach
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
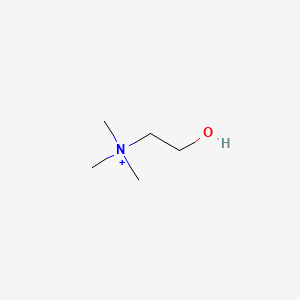
| Gut–Brain Axis & Enteric Nervous System (ENS) | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Choline is metabolised by gut bacteria; some strains (e.g. Lactobacillus) can produce acetylcholine. Microbial choline metabolism (e.g. trimethylamine) shows inter-individual variability and may influence host metabolism and gut–brain signalling. | |
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Choline-derived betaine supports homocysteine remethylation; elevated homocysteine is linked to oxidative stress and inflammatory signalling. Phosphatidylcholine supports membrane integrity and cell signalling in immune and redox contexts. | |
| Metabolic & Neuroendocrine Stress (HPA Axis & ANS) | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Choline supports hepatic VLDL assembly and lipid export; methyl donors (choline, betaine) may influence adenosine metabolism and HPA axis activity. Adequate choline status supports metabolic stability and stress physiology. | |
| Methylation & One-Carbon Metabolism | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Precursor to trimethylglycine (TMG/betaine), a dietary methyl donor that helps recycle homocysteine to methionine via an alternative pathway; supports one-carbon metabolism alongside folate, riboflavin, and B12; influences methylation dynamics relevant to MTHFR and COMT activity | |
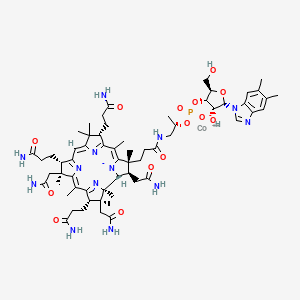
| Methylation & One-Carbon Metabolism | Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential cofactor in remethylation of homocysteine to methionine, which is converted to S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe); works with B6, B2, and folate; contributes meaningfully to homocysteine reduction, especially in combination with omega-3 fatty acids | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Phosphatidylcholine and other choline-containing phospholipids support mitochondrial membrane integrity and energy metabolism; choline-derived betaine contributes to one-carbon status that can influence mitochondrial resilience | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Iron | Contextual / minor contributor | Critical for oxygen delivery to the brain via hemoglobin; supports mitochondrial function and energy production | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Crucial role in conversion of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA, a key step in mitochondrial energy production; deficiency leads to buildup of methylmalonic acid and odd-chain fatty acids, which are neurotoxic | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential precursor for acetylcholine synthesis, supporting memory, learning, and neuroplasticity; supports membrane phospholipid biosynthesis (PC) which is critical for membrane fluidity and neurotransmitter receptor function; phospholipid methylation (PLM) alters membrane structure, facilitating faster neuronal recovery and influencing ion channel behavior in gamma oscillations linked to attention and cognition | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Iron | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential cofactor for tyrosine hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in the conversion of tyrosine to dopamine; critical for catecholamine synthesis | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports neurotransmitter production through methylation; essential for myelin synthesis |
References
- Organ meats (heart, liver), oily fish (sardines, mackerel), beef are top sources for CoQ10; organ meats are the highest dietary source of CoQ10 (up to 12mg per 100g)
- Occasional offal (Latoch et al. 2024) i.e. liver recommended for nutrient density
- Ethically sourced, high-nutrient-density options (e.g., liver, fish roe, sardines)