Salmon Roe
Overview
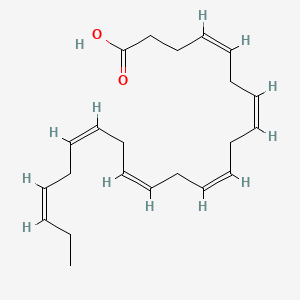
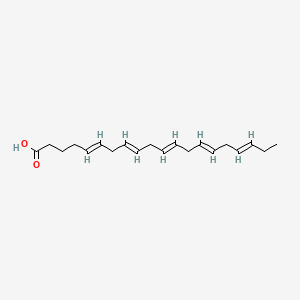
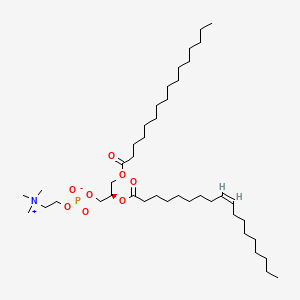
Salmon roe (fish eggs) provides omega-3 fatty acids in phospholipid-bound form, which enhances brain delivery compared to triglyceride forms. It provides DHA, EPA, phospholipids, choline, and astaxanthin with high bioavailability and zero oxidation risk. Studies show phospholipid-bound omega-3s such as krill oil and fish roe provide EPA/DHA in a phospholipid form that gets easily converted to lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), which was 1.9-fold more efficacious for brain gray matter DHA accretion in porcine models compared to triglyceride forms.
Astaxanthin (naturally occurring)
Salmon roe contains astaxanthin, a lipid-soluble carotenoid that contributes to the stability of omega-3–rich membranes. In food matrices such as roe, astaxanthin helps limit oxidative stress associated with highly unsaturated fats and supports mitochondrial and cellular resilience.
Recipes
Substances
Vitamins & Minerals
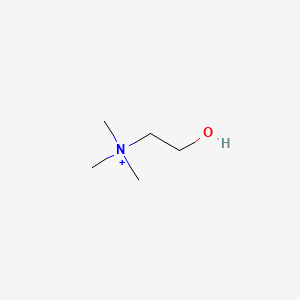
Salmon roe is exceptionally rich in essential vitamins and minerals. It is one of the best dietary sources of vitamin B12, providing over 330% of the daily value per 100 grams. Salmon roe is also an excellent source of vitamin D (58% DV), supporting immune function and calcium homeostasis. It provides substantial amounts of selenium (94% DV) for antioxidant enzyme function, magnesium (75% DV) for neurotransmitter synthesis and mitochondrial function, and iron (66% DV) for oxygen transport and dopamine synthesis. Additional B vitamins include choline (45% DV), pantothenic acid (B5), riboflavin (B2), pyridoxine (B6), and folate. Salmon roe also provides calcium (28% DV), vitamin E (13% DV), and phosphorus (39% DV), making it one of the most nutrient-dense foods available.
Preparation Notes
- Best consumed cold/raw (sushi, spoonful daily) to preserve phospholipid structure
- Avoid cooking to preserve phospholipid structure and prevent oxidation
- Zero oxidation risk when fresh
- DHA or EPA incorporated into PC and converted into lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) crosses the blood-brain barrier far more efficiently than free fatty acid or triglyceride-bound forms Patrick 2019
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gut–Brain Axis & Enteric Nervous System (ENS) | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Choline is metabolised by gut bacteria; some strains (e.g. Lactobacillus) can produce acetylcholine. Microbial choline metabolism (e.g. trimethylamine) shows inter-individual variability and may influence host metabolism and gut–brain signalling. | |
| Gut–Brain Axis & Enteric Nervous System (ENS) | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Contextual / minor contributor | — | |
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Choline-derived betaine supports homocysteine remethylation; elevated homocysteine is linked to oxidative stress and inflammatory signalling. Phosphatidylcholine supports membrane integrity and cell signalling in immune and redox contexts. | |
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Contextual / minor contributor | Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators (SPMs) - resolvins, protectins, maresins terminate inflammation without immunosuppression, downregulate COX-2, inhibit neutrophil infiltration, enhance macrophage clearance, limit glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. Production of DHEA and EPEA (N-acyl ethanolamines) feeds into CB2-related anti-inflammatory signalling; ECS lipid mediators regulate immune tone and microglial activation (primary anchor for ECS mechanism: Inflammation & Oxidative Stress). | |
| Metabolic & Neuroendocrine Stress (HPA Axis & ANS) | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Choline supports hepatic VLDL assembly and lipid export; methyl donors (choline, betaine) may influence adenosine metabolism and HPA axis activity. Adequate choline status supports metabolic stability and stress physiology. | |
| Metabolic & Neuroendocrine Stress (HPA Axis & ANS) | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Contextual / minor contributor | Improve vagal tone and HRV control, improve cortisol rhythms | |
| Methylation & One-Carbon Metabolism | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Precursor to trimethylglycine (TMG/betaine), a dietary methyl donor that helps recycle homocysteine to methionine via an alternative pathway; supports one-carbon metabolism alongside folate, riboflavin, and B12; influences methylation dynamics relevant to MTHFR and COMT activity | |
| Methylation & One-Carbon Metabolism | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Contextual / minor contributor | Support homocysteine reduction in combination with B12, phospholipid methylation (PLM) dependent on SAMe | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Astaxanthin | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports mitochondrial and cellular resilience through antioxidant protection | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Phosphatidylcholine and other choline-containing phospholipids support mitochondrial membrane integrity and energy metabolism; choline-derived betaine contributes to one-carbon status that can influence mitochondrial resilience | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Contextual / minor contributor | ECS-related lipid signalling may influence mitochondrial coupling/efficiency (context-dependent; largely preclinical). Omega-3 incorporation changes membrane fluidity (secondary anchor for ECS mechanism: Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics). | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Choline | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential precursor for acetylcholine synthesis, supporting memory, learning, and neuroplasticity; supports membrane phospholipid biosynthesis (PC) which is critical for membrane fluidity and neurotransmitter receptor function; phospholipid methylation (PLM) alters membrane structure, facilitating faster neuronal recovery and influencing ion channel behavior in gamma oscillations linked to attention and cognition | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Contextual / minor contributor | Membrane fluidity and neurotransmitter receptor function, ion channel behavior and gamma oscillations, support neurotransmission and phospholipid methylation | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Phosphatidylcholine (PC) | Contextual / minor contributor | Major neuronal membrane phospholipid central to membrane fluidity, receptor function, and acetylcholine synthesis; DHA/EPA incorporated into PC are converted to lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), a key transport form across the BBB |
References
- Salmon Roe: DHA, EPA, phospholipids, choline, astaxanthin; highly bioavailable; zero oxidation risk
- Targeted foods such as salmon or lumpfish roe can be used to reliably and safely exceed minimum intakes
- DHA or EPA incorporated into PC and converted into lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) crosses the blood-brain barrier far more efficiently than free fatty acid or triglyceride-bound forms Patrick 2019
- Phospholipid-bound omega-3s such as krill oil and fish roe provide EPA/DHA in a phospholipid form that gets easily converted to LPC was 1.9-fold more efficacious for brain gray matter DHA accretion in porcine models Liu et al. 2014
- Acetylcholine and choline: Memory, learning, neuroplasticity; food sources include egg yolks, fish roe, soy, wheat germ, liver