Black Goji
Overview
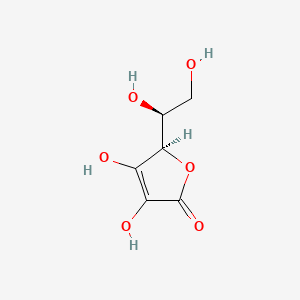
Black goji berries provide high levels of C3G (cyanidin-3-glucoside) anthocyanins that chelate heavy metals and support neuroprotection. Anthocyanins, especially C3G-rich sources like berries, purple potatoes, and black goji, serve as natural chelation agents for heavy metals and environmental contaminants, neuroprotective molecules that support synaptic resilience and detox pathways, and detox allies against microplastics and hormone-disrupting pollutants.
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Can be consumed dried or fresh
- Part of diverse polyphenol intake
- Supports detoxification pathways
- Pair with other C3G-rich foods
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Vitamin C (Ascorbate) | Contextual / minor contributor | Antioxidant properties; supports anti-inflammatory effects | |
| Metabolic & Neuroendocrine Stress (HPA Axis & ANS) | Vitamin C (Ascorbate) | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports stress response through antioxidant and neurochemical effects | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Vitamin C (Ascorbate) | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports norepinephrine synthesis; transported in brain via SVCT2 |
References
- Anthocyanins, especially C3G-rich sources like berries, purple potatoes, and black goji, serve as: Natural chelation agents for heavy metals and environmental contaminants; Neuroprotective molecules that support synaptic resilience and detox pathways; Detox allies against microplastics and hormone-disrupting pollutants