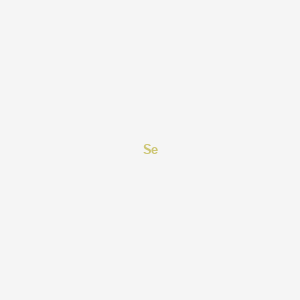Sardines
Overview
Sardines are small, sustainable oily fish providing EPA/DHA omega-3s, CoQ10, calcium (from bones), and B vitamins with low heavy metal burden. Sardines are listed as top animal sources for omega-3 (EPA/DHA) and CoQ10, supporting brain health and mitochondrial function. Regular consumption of oily fish to meet baseline omega-3 requirements (~250–500 mg/day EPA+DHA) is recommended.
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Low on food chain = lower heavy metal burden compared to larger predatory fish
- Can be consumed with bones for calcium content
- Best prepared with gentle cooking to preserve omega-3s and prevent oxidation
- Sustainable and affordable omega-3 source
- Ethically sourced, high-nutrient-density option
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gut–Brain Axis & Enteric Nervous System (ENS) | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Contextual / minor contributor | — | |
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Contextual / minor contributor | Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators (SPMs) - resolvins, protectins, maresins terminate inflammation without immunosuppression, downregulate COX-2, inhibit neutrophil infiltration, enhance macrophage clearance, limit glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. Production of DHEA and EPEA (N-acyl ethanolamines) feeds into CB2-related anti-inflammatory signalling; ECS lipid mediators regulate immune tone and microglial activation (primary anchor for ECS mechanism: Inflammation & Oxidative Stress). | |
| Metabolic & Neuroendocrine Stress (HPA Axis & ANS) | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Contextual / minor contributor | Improve vagal tone and HRV control, improve cortisol rhythms | |
| Methylation & One-Carbon Metabolism | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Contextual / minor contributor | Support homocysteine reduction in combination with B12, phospholipid methylation (PLM) dependent on SAMe | |
| Methylation & One-Carbon Metabolism | Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential cofactor in remethylation of homocysteine to methionine, which is converted to S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe); works with B6, B2, and folate; contributes meaningfully to homocysteine reduction, especially in combination with omega-3 fatty acids | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Contextual / minor contributor | ECS-related lipid signalling may influence mitochondrial coupling/efficiency (context-dependent; largely preclinical). Omega-3 incorporation changes membrane fluidity (secondary anchor for ECS mechanism: Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics). | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Selenium | Contextual / minor contributor | Protects mitochondria from oxidative damage through antioxidant enzyme activity | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Crucial role in conversion of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA, a key step in mitochondrial energy production; deficiency leads to buildup of methylmalonic acid and odd-chain fatty acids, which are neurotoxic | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Vitamin B3 (Niacin; Niacinamide) | Contextual / minor contributor | Replenishes NAD+, supporting oxidative phosphorylation, sirtuin signaling, and mitochondrial biogenesis; key for neuronal energy metabolism | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Calcium | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential for nerve impulse transmission and neurotransmission | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Contextual / minor contributor | Membrane fluidity and neurotransmitter receptor function, ion channel behavior and gamma oscillations, support neurotransmission and phospholipid methylation | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports neurotransmitter production through methylation; essential for myelin synthesis |
References
- Oily fish (sardines, mackerel), beef for CoQ10; supports mitochondrial electron transport and antioxidant protection for neurons
- EPA & DHA (Omega-3): Sardines, mackerel, salmon, tuna, cod liver; anti-inflammatory; membrane fluidity; neurotransmitter receptor function
- Listed as top animal source for omega-3 (EPA/DHA)
- Ethically sourced, high-nutrient-density options (e.g., liver, fish roe, sardines)
- Regular consumption of oily fish to meet baseline omega-3 requirements (~250–500 mg/day EPA+DHA)