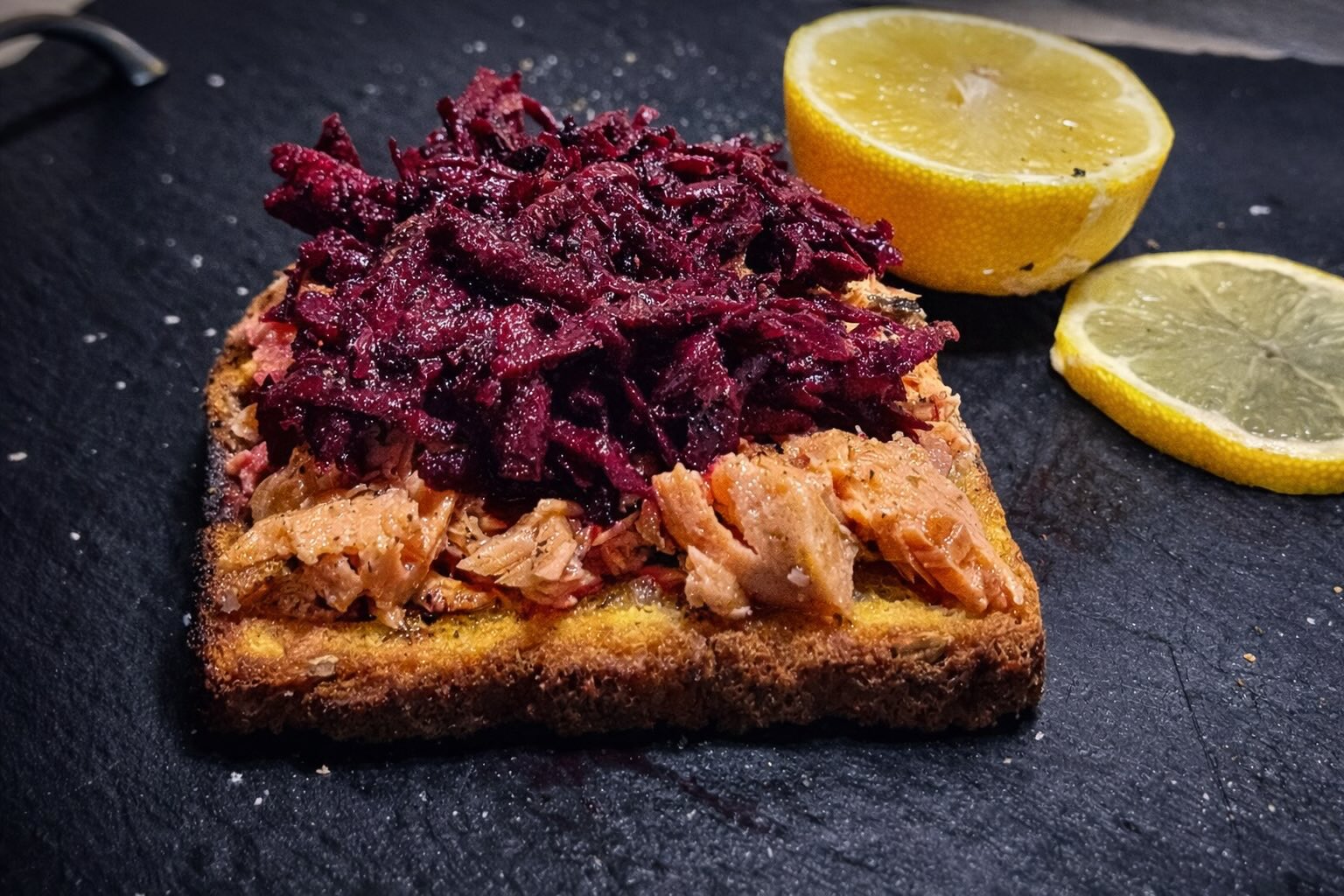
Sourdough Bread
Overview
Sourdough bread, especially when made with quinoa or other functional flours, provides GABA, improved amino acid bioavailability, and optimized Maillard reaction products (MRPs) with reduced acrylamide. Quinoa sourdough offers both very high nutrients (due to the quinoa) and a high GABA profile, and sourdough fermentation enhances bioavailability of amino acids through activation of endogenous cereal proteases.
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Use whole grain or pseudograin flours for higher nutrient content
- Long fermentation (12-18h) improves amino acid release
- Dutch oven baking reduces acrylamide formation
- Glycine addition (0.3-0.4%) further reduces acrylamide
- Traditionally fermented breads optimize Maillard Reaction Products (MRPs)
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Copper | Contextual / minor contributor | Participates in redox enzymes and antioxidant networks | |
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Zinc | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports immune signaling; gut barrier integrity disrupted by nutrient deficiencies including zinc | |
| Metabolic & Neuroendocrine Stress (HPA Axis & ANS) | Magnesium | Contextual / minor contributor | Helps manage stress responses; combined with vitamin D reduced behavioral problems; synergy with zinc and omega-3s reported | |
| Methylation & One-Carbon Metabolism | Zinc | Contextual / minor contributor | Deficiencies in vitamins and minerals essential for methylation, such as folate, vitamin B12, and zinc, are correlated to ADHD symptoms; supplementing these micronutrients has shown potential in supporting methylation and reducing symptom severity | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Iron | Contextual / minor contributor | Critical for oxygen delivery to the brain via hemoglobin; supports mitochondrial function and energy production | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Magnesium | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports enzymes involved in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle (processes that generate ATP from glucose); binds to ATP and all triphosphates in cells to activate them | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Manganese | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports mitochondrial antioxidant defense through MnSOD activity | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Copper | Contextual / minor contributor | Cofactor in dopamine β-hydroxylase, supporting catecholamine synthesis; supports norepinephrine synthesis | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Iron | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential cofactor for tyrosine hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in the conversion of tyrosine to dopamine; critical for catecholamine synthesis | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Magnesium | Contextual / minor contributor | Broad cofactor for neurotransmitter synthesis and receptor modulation (e.g., NMDA, GABA); functions as an NMDA receptor antagonist and GABA receptor modulator; assists enzymes involved in synthesis of dopamine and serotonin | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Potassium | Contextual / minor contributor | Critical for membrane potential, nerve signaling, and neuronal excitability; adequate intake balances sodium effects | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Zinc | Contextual / minor contributor | Important for DNA synthesis, cell division, and neurotransmitter regulation, particularly in modulating dopamine—a key neurotransmitter implicated in ADHD; acts as an allosteric modulator of the GABA receptor; supports glutamate regulation |
References
- Quinoa sourdough offers both very high nutrients (due to the quinoa) and a high GABA profile
- Sourdough fermentation enhances bioavailability of amino acids through activation of endogenous cereal proteases Gänzle, Loponen, and Gobbetti 2008
- Traditionally fermented breads that optimize Maillard Reaction Products (MRPs)
- Nicotinamide Riboside: Dairy milk, whey protein, yeast-containing foods (e.g., sourdough bread)