Fortified Plant Milks
Overview
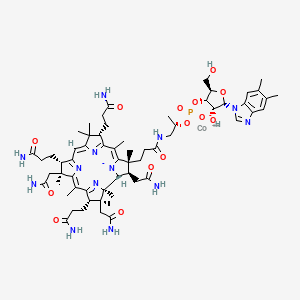
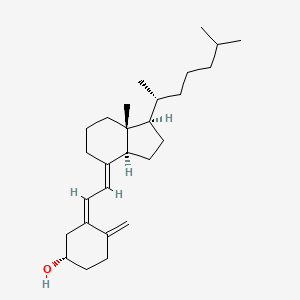
Fortified plant milks (soy, almond, oat, etc.) provide essential nutrients like B12, vitamin D, and sometimes iodine, helping close vegan nutrient gaps. Targets foods providing essential brain supporting vitamins: D (UV-exposed mushrooms; fortified plant milks/yogurts), B12 (fortified plant milks, nutritional yeast).
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Choose fortified varieties for B12 and D
- Check fortification levels and forms (methylcobalamin for B12)
- Important for vegan/vegetarian nutrient sufficiency
- Part of functional food strategy
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gut–Brain Axis & Enteric Nervous System (ENS) | Vitamin D | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports gut barrier integrity; nutrient deficiencies including vitamin D disrupt tight junctions, increasing permeability | |
| Metabolic & Neuroendocrine Stress (HPA Axis & ANS) | Vitamin D | Contextual / minor contributor | Modulates immune responses to reduce inflammation in the brain; supports stress response through neurotrophic and immune effects | |
| Methylation & One-Carbon Metabolism | Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential cofactor in remethylation of homocysteine to methionine, which is converted to S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe); works with B6, B2, and folate; contributes meaningfully to homocysteine reduction, especially in combination with omega-3 fatty acids | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Crucial role in conversion of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA, a key step in mitochondrial energy production; deficiency leads to buildup of methylmalonic acid and odd-chain fatty acids, which are neurotoxic | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Calcium | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential for nerve impulse transmission and neurotransmission | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Iodine | Contextual / minor contributor | Thyroid hormones regulate synthesis and regulation of key neurotransmitters (dopamine and serotonin), supporting cognitive function and development | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports neurotransmitter production through methylation; essential for myelin synthesis |
References
- Fortified plant milks and dairy milk can help meet calcium (and sometimes iodine, depending on fortification and local practices) targets
- Targets foods providing essential brain supporting vitamins: D (UV-exposed mushrooms; fortified plant milks/yogurts), B12 (fortified plant milks, nutritional yeast)
- Vitamin B12: Fortified plant milks, nutritional yeast, supplements