Lamb
Overview
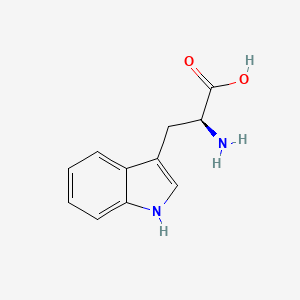
Lamb provides creatine, heme iron, and complete high-quality protein, supporting ATP recycling and neurotransmitter synthesis. Creatine: Supports ATP recycling in neurons; enhances working memory and cognitive processing speed; food sources include beef, lamb, pork, salmon, tuna, cod, scallops. Iron (heme & non-heme): Oxygen delivery to brain, dopamine synthesis; food sources include liver, beef, lamb, poultry, fish. Heme iron is 2-3× more bioavailable than non-heme iron.
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Choose grass-fed when possible for better fatty acid profile
- Gentle cooking preserves nutrients and prevents formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs)
- Important for creatine and heme iron intake
- Part of diverse protein strategy
- Supports neurotransmitter synthesis through tryptophan and tyrosine content
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
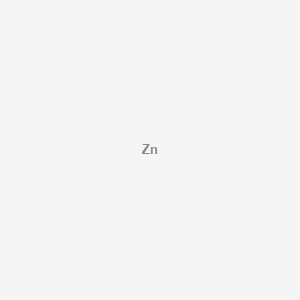
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Zinc | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports immune signaling; gut barrier integrity disrupted by nutrient deficiencies including zinc | |
| Methylation & One-Carbon Metabolism | Zinc | Contextual / minor contributor | Deficiencies in vitamins and minerals essential for methylation, such as folate, vitamin B12, and zinc, are correlated to ADHD symptoms; supplementing these micronutrients has shown potential in supporting methylation and reducing symptom severity | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Creatine | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports ATP recycling via phosphocreatine system; buffers high-energy demand in neurons; enhances mitochondrial energy buffering | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Iron | Contextual / minor contributor | Critical for oxygen delivery to the brain via hemoglobin; supports mitochondrial function and energy production | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Iron | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential cofactor for tyrosine hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in the conversion of tyrosine to dopamine; critical for catecholamine synthesis | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Tryptophan | Contextual / minor contributor | Precursor for serotonin and melatonin; brain entry competes at LAT1 with other large neutral amino acids (LNAAs); carbohydrate-rich, low-protein meals raise the plasma tryptophan:LNAA ratio because insulin pushes competing LNAAs out to muscles; can feed NAD+ synthesis via the kynurenine pathway | |
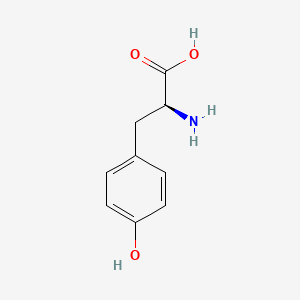
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Tyrosine | Contextual / minor contributor | Catecholamine precursor (dopamine, norepinephrine); brain transport via LAT1 competes with other LNAAs; iron is an essential cofactor for tyrosine hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in conversion of tyrosine to dopamine; cofactors include iron, B6, folate, omega-3s, and BH₄ (tetrahydrobiopterin) to support rate-limiting steps in catecholamine synthesis | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Zinc | Contextual / minor contributor | Important for DNA synthesis, cell division, and neurotransmitter regulation, particularly in modulating dopamine—a key neurotransmitter implicated in ADHD; acts as an allosteric modulator of the GABA receptor; supports glutamate regulation |
References
- Creatine: Supports ATP recycling in neurons; enhances working memory and cognitive processing speed; food sources include beef, lamb, pork, salmon, tuna, cod, scallops
- Iron (heme & non-heme): Oxygen delivery to brain, dopamine synthesis; food sources include liver, beef, lamb, poultry, fish
- Heme iron is 2-3× more bioavailable than non-heme iron, making animal sources important for iron status
- Zinc: Neurotransmitter modulation, synaptic plasticity, antioxidant enzymes; food sources include oysters, beef, crab, chicken, pork (lamb also contains)