Green Tea
Overview
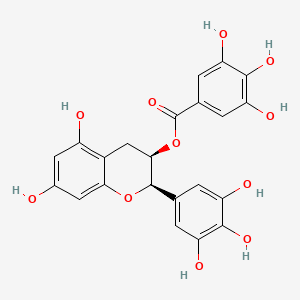
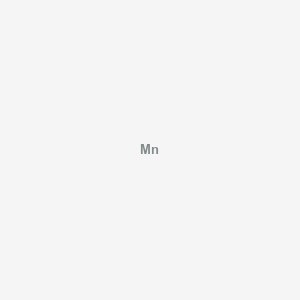
Green tea provides catechins (especially EGCG), L-theanine, and polyphenols that support cognitive function, antioxidant defenses, and metabolic health. Green tea contributes manganese and small amounts of fluoride and potassium, alongside polyphenols that support antioxidant defenses. Green tea catechins (e.g., EGCG, EGC) contribute to visceral adipose tissue reduction and neuroprotective effects in Green Mediterranean Diet studies, which showed attenuated brain atrophy by ~50%. Green tea is also mentioned as a polyphenol antimicrobial for SIBO suppression.
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Steep at lower temperatures to preserve catechins and prevent degradation
- Can reduce non-heme iron absorption if taken with meals; space ≥1 hour from iron-rich meals or add lemon (vitamin C) to mitigate this
- Green tea catechins increase Faecalibacterium and Roseburia; inhibit Enterobacteriaceae; reduce NF-κB activation
- L-theanine found in green tea increases alpha waves and calms without sedation
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gut–Brain Axis & Enteric Nervous System (ENS) | EGCG (Green Tea Catechin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Green tea catechins increase Faecalibacterium and Roseburia; inhibit Enterobacteriaceae; reduce NF-κB activation | |
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | EGCG (Green Tea Catechin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Polyphenol antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects; reduces inflammatory signaling | |
| Metabolic & Neuroendocrine Stress (HPA Axis & ANS) | EGCG (Green Tea Catechin) | Contextual / minor contributor | Contributes to stress buffering through polyphenol effects | |
| Metabolic & Neuroendocrine Stress (HPA Axis & ANS) | L-Theanine | Contextual / minor contributor | Increases alpha waves and promotes calm without sedation; supports relaxation | |
| Mitochondrial Function & Bioenergetics | Manganese | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports mitochondrial antioxidant defense through MnSOD activity | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | L-Theanine | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports GABAergic tone and neurotransmitter balance | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Potassium | Contextual / minor contributor | Critical for membrane potential, nerve signaling, and neuronal excitability; adequate intake balances sodium effects |
References
- Green tea contributes manganese and small amounts of fluoride and potassium, alongside polyphenols that support antioxidant defenses
- Green tea catechins (e.g., EGCG, EGC) contribute to visceral adipose tissue reduction and neuroprotective effects in Green Mediterranean Diet studies Zelicha et al. 2022
- Green Mediterranean Diet attenuated brain atrophy by ~50%, with glycemic control contributing to the neuroprotective signal, consistent with polyphenol–fibre–microbiome synergy Pachter et al. 2024
- Polyphenol antimicrobials (berberine, oregano, green tea) for SIBO suppression
- Exercise-induced BDNF surges can be potentiated by polyphenols (e.g., blueberries, green tea)
- Polyphenol sources including green tea catechins increase Faecalibacterium and Roseburia; inhibit Enterobacteriaceae; reduce NF-κB activation
- GABA: Main inhibitory neurotransmitter; food sources include green tea, fermented foods, polyphenols (genistein), spinach, almonds, pumpkin seeds