Cabbage
Overview
Cabbage provides fiber, vitamin C, and is the base for sauerkraut fermentation, supporting gut health through both fresh and fermented forms. Sauerkraut is fermented cabbage, rich in Lactobacillus, and is part of the fermented foods strategy.
Recipes
Substances
Preparation Notes
- Can be consumed fresh or fermented
- Fermentation (sauerkraut) provides probiotics
- Part of diverse vegetable intake
- Supports gut health
Biological Target Matrix
| Biological Target | Substance | Contribution Level | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
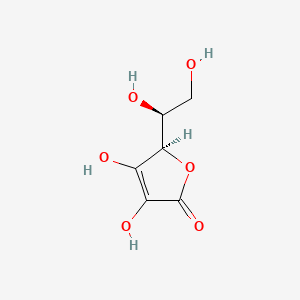
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Vitamin C (Ascorbate) | Contextual / minor contributor | Antioxidant properties; supports anti-inflammatory effects | |
| Metabolic & Neuroendocrine Stress (HPA Axis & ANS) | Vitamin C (Ascorbate) | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports stress response through antioxidant and neurochemical effects | |
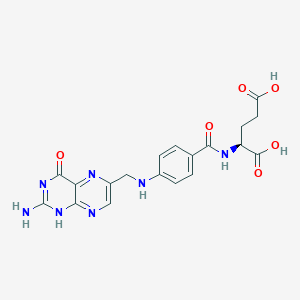
| Methylation & One-Carbon Metabolism | Vitamin B9 (Folate; 5-MTHF) | Contextual / minor contributor | Essential cofactor in remethylation of homocysteine to methionine, which is converted to S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe); SAMe fuels synthesis of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin and drives phospholipid methylation in neuronal membranes | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Vitamin B9 (Folate; 5-MTHF) | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports neurotransmitter synthesis through methylation; cofactor for dopamine synthesis alongside iron, B6, and omega-3s | |
| Neurotransmitter Regulation | Vitamin C (Ascorbate) | Contextual / minor contributor | Supports norepinephrine synthesis; transported in brain via SVCT2 |
References
- Sauerkraut: Fermented cabbage, rich in Lactobacillus