Substances Index
This page organizes all substances referenced in the BRAIN Diet documentation according to their biological classification: Nutrients (essential), Bioactive Compounds (non-essential, functional), and Microbial Metabolites (derived from digestion or microbial action).
Nutrients (Essential + Classical)
Macronutrients
Amino Acids
Essential Amino Acids
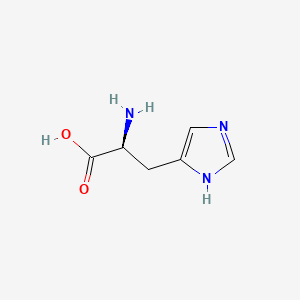
Histidine
Essential AA; precursor to histamine; roles in enzyme active sites
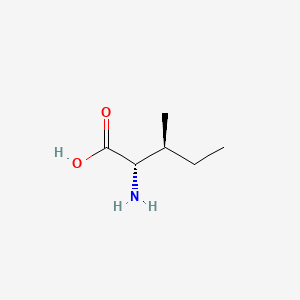
Isoleucine
Essential BCAA; energy metabolism; complements leucine/valine
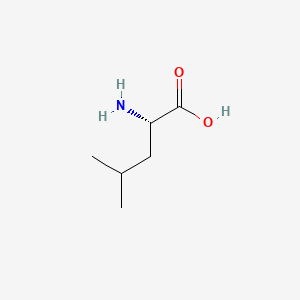
Leucine
Essential BCAA; mTOR signaling; protein synthesis; cognitive load support
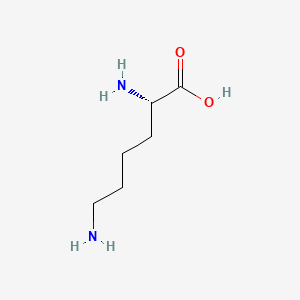
Lysine
Essential AA; limiting in many cereals; complements legumes
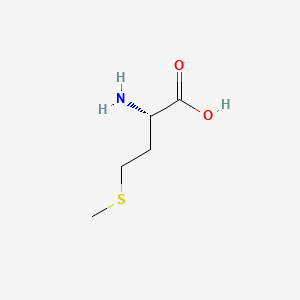
Methionine
Essential AA; precursor to SAMe via methylation cycle
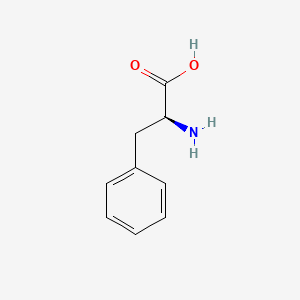
Phenylalanine
Essential AA; precursor to tyrosine → catecholamines
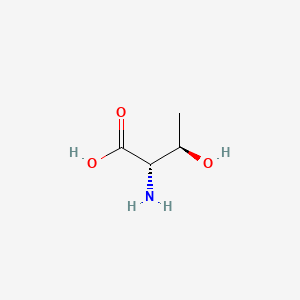
Threonine
Essential AA; structural proteins; mucin production
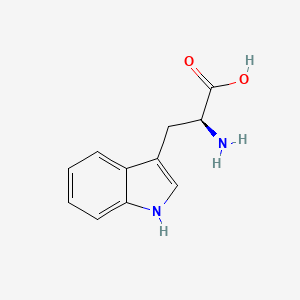
Tryptophan
Serotonin/melatonin precursor; NAD+ pathway substrate; LAT1 transport dynamics
Valine
Essential BCAA; supports protein balance and neurotransmitter transport competition
Conditional Amino Acids
Arginine
Conditionally essential amino acid; precursor for creatine and nitric oxide synthesis
Glycine
Nonessential amino acid; inhibitory neurotransmitter; supports sleep, gut barrier repair, and glutathione production
Tyrosine
Dopamine and norepinephrine precursor; LAT1 competition with LNAAs
Fatty Acids
Saturated Fatty Acids
Capric Triglyceride (Tridecanoin)
Medium-chain triglyceride (C10) providing rapid brain energy via ketone production
Caproic Triglyceride (Tricaproin)
Medium-chain triglyceride (C6) providing rapid brain energy via ketone production
Caprylic Triglyceride (Trioctanoin)
Medium-chain triglyceride (C8) providing rapid brain energy via ketone production
MCT (Medium-Chain Triglycerides)
Medium-chain fatty acids (C8, C10) providing rapid brain energy via ketone production
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs)
PUFAs include Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid)
Essential omega-3 precursor; limited conversion to DHA/EPA
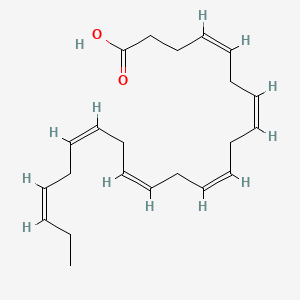
DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid)
Accounts for ~10–15% of total brain fatty acids, 20–30% of neuronal phospholipids (PE, PS), and >90% of brain omega-3 PUFA; critical for membrane fluidity, synaptic vesicle fusion, neurodevelopment
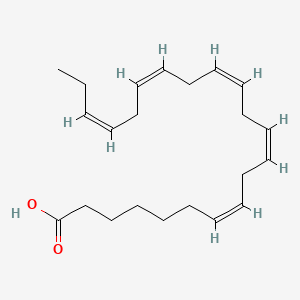
DPA (Docosapentaenoic Acid)
The "intermediate" between EPA ↔ DHA; important in vascular health, repair, and immune modulation
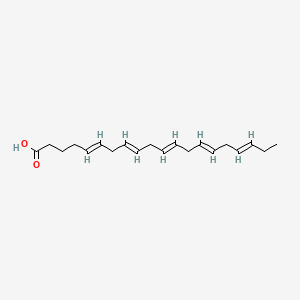
EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid)
Potent anti-inflammatory; precursor to E-series resolvins; modulates dopamine and serotonin signalling
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
(EPA, DHA) Anti-inflammatory, membrane, and neuromodulatory lipids central to BRAIN Diet
Omega-6 Fatty Acids
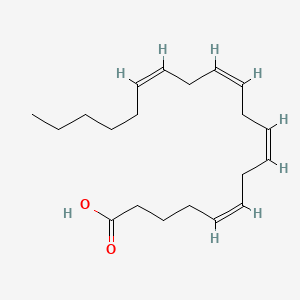
Arachidonic Acid (AA, n-6)
Omega-6 PUFA; eicosanoid precursor; balance with omega-3s
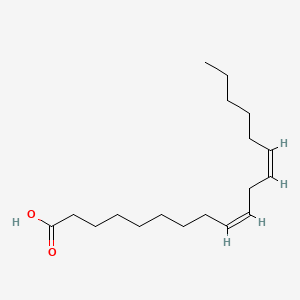
Linoleic Acid (LA, n-6)
Essential omega-6; precursor to arachidonic acid and eicosanoids
Phospholipids
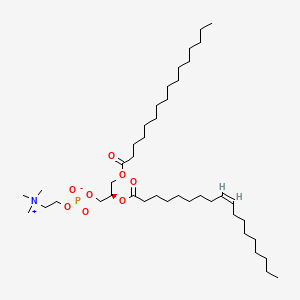
Phosphatidylcholine (PC)
Key brain phospholipid; carrier for DHA/EPA and acetylcholine precursor pathway
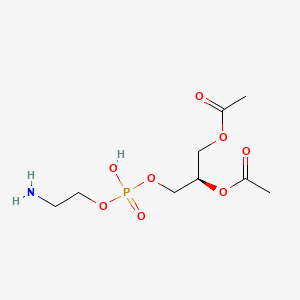
Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE)
Brain phospholipid; precursor to PC and NAPE → NAEs (PEA/OEA/AEA)
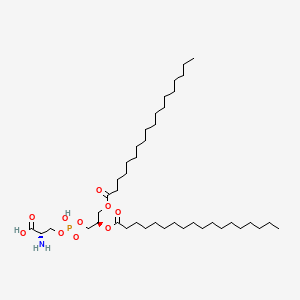
Phosphatidylserine (PS)
Neuronal membrane phospholipid; cognition; stress modulation
Micronutrients
Vitamins
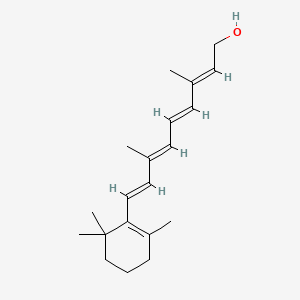
Vitamin A (Retinoids; β-Carotene precursor)
Neurodevelopment; immune regulation; antioxidant via carotenoids
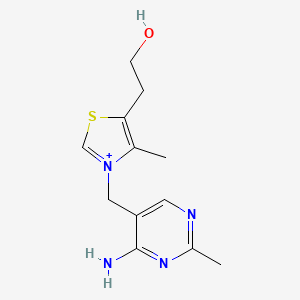
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
Mitochondrial glucose metabolism; ATP synthesis; rapid turnover in CNS
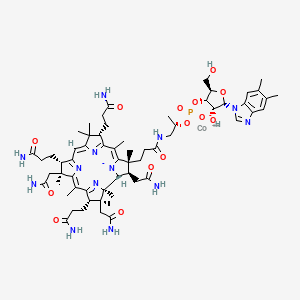
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
Methylation; myelin; mitochondrial odd-chain FA metabolism
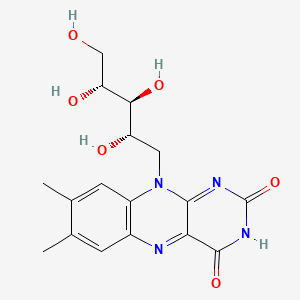
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
FMN/FAD coenzymes; redox balance; supports methylation via MTHFR
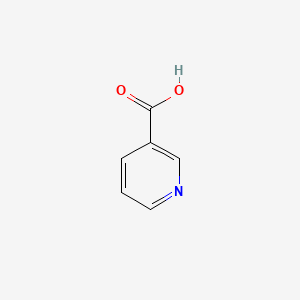
Vitamin B3 (Niacin; Niacinamide)
NAD+ precursor; supports mitochondrial biogenesis and ATP production
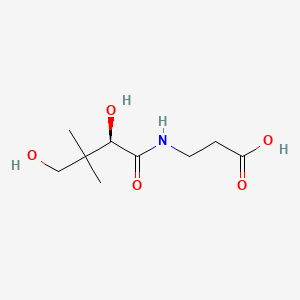
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
CoA synthesis; fatty-acid oxidation; TCA cycle flux
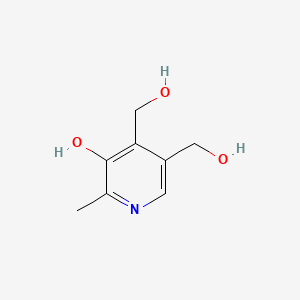
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine → PLP)
PLP cofactor for neurotransmitter synthesis; relies on brain PDXK activation
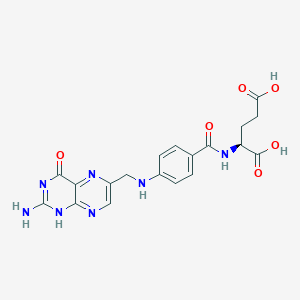
Vitamin B9 (Folate; 5-MTHF)
One-carbon metabolism; methylation; homocysteine recycling
Vitamin C (Ascorbate)
Antioxidant; supports iron absorption; neuronal SVCT2 transport
Vitamin D
Neurotrophic and immune modulation; calcium homeostasis
Vitamin E (Tocopherols/Tocotrienols)
Lipid-phase antioxidant; protects PUFA (DHA) in membranes
Vitamin K2 (MK forms)
Calcium handling; potential roles in brain health; often co-occurs with fat-soluble vitamins
Minerals
Macro Minerals

Calcium
Bone health; neurotransmission; interacts with vitamin D and K2
Magnesium
Enzymatic cofactor (>300 reactions); neurotransmitters; mitochondria; redox balance

Potassium
Electrolyte for nerve transmission, muscle function, and blood pressure regulation

Sodium
Electrolyte for fluid balance and nerve function
Trace Minerals

Copper
Cofactor in redox enzymes; dopamine β-hydroxylase; iron metabolism interplay

Iodine
Thyroid hormone synthesis; neurodevelopment; neurotransmitter regulation

Iron
Oxygen transport; dopamine synthesis (tyrosine hydroxylase cofactor)
Manganese
Cofactor for MnSOD (SOD2); mitochondrial antioxidant defense
Selenium
Antioxidant enzyme cofactor (GPx); supports redox balance
Zinc
Cofactor in neurotransmission and antioxidant enzymes; dopamine modulation
Bioactive Compounds (Non-Essential, Functional)
Polyphenols
Flavonoids
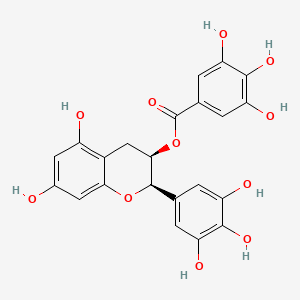
EGCG (Green Tea Catechin)
Polyphenol; antioxidant; gut barrier/LPS modulation; supports microbiome
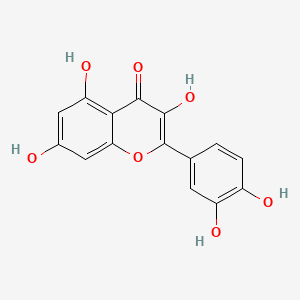
Quercetin (and Isoquercetin)
Polyphenol; antioxidant; mitochondrial support; bioavailability improved with vitamin C
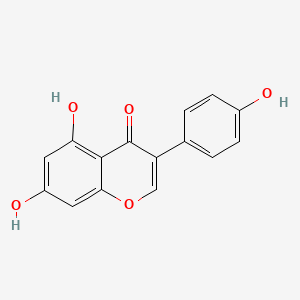
Genistein
Soy isoflavone; ECS modulation via FAAH inhibition; anti-inflammatory/neuroprotective
Flavan-3-ols

EGCG (Green Tea Catechin)
Polyphenol; antioxidant; gut barrier/LPS modulation; supports microbiome
Flavonols

Quercetin (and Isoquercetin)
Polyphenol; antioxidant; mitochondrial support; bioavailability improved with vitamin C
Isoflavones

Genistein
Soy isoflavone; ECS modulation via FAAH inhibition; anti-inflammatory/neuroprotective
Phenolic Acids
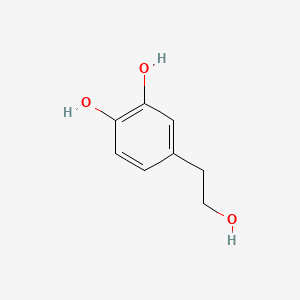
Hydroxytyrosol (Olive Polyphenol)
Potent antioxidant polyphenol from extra-virgin olive oil; anti-inflammatory
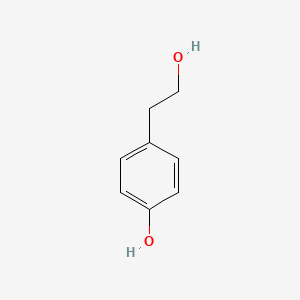
Tyrosol
Phenolic compound in olive oil; neuroprotective effects and precursor to hydroxytyrosol
Secoiridoids
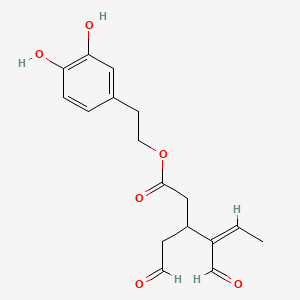
Oleacein
Secoiridoid polyphenol in extra-virgin olive oil; antioxidant and NRF2 activation
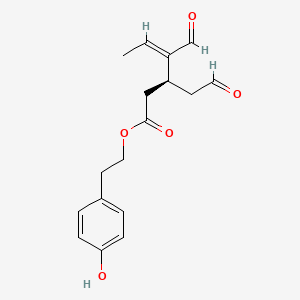
Oleocanthal
Secoiridoid polyphenol in extra-virgin olive oil; NF-κB inhibition and anti-inflammatory effects
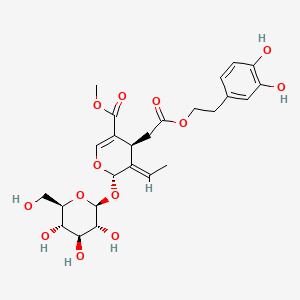
Oleuropein
Major secoiridoid polyphenol in olive oil; oleuropein aglycone supports mitophagy, SIRT1, and AMPK activation
Carotenoids
Astaxanthin
Lipid-soluble carotenoid that stabilizes omega-3–rich membranes; supports mitochondrial and cellular resilience
β-Carotene
Neuroprotective carotenoid; vitamin A precursor; supports immune regulation and neuronal development
Lutein
Neuroprotective carotenoid; accumulates in neural tissues and retina; supports cognitive performance
Lycopene
Neuroprotective carotenoid; found in tomatoes; absorption enhanced by cooking and dietary fat
Zeaxanthin
Neuroprotective carotenoid; accumulates in neural tissues and retina; supports cognitive performance
Terpenes & Terpenoids
Saffron (Crocin, Safranal)
Mood and cognition support; sensitive to heat/light; culinary-first use
Lipid-Based Compounds
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)
Electron transport chain cofactor and antioxidant relevant to mitochondrial function
Creatine
Phosphocreatine system buffer for neuronal ATP demand; cognitive support evidence
Alkaloids
Berberine
Polyphenolic alkaloid; glycemic control; antimicrobial effects; microbiome modulation
L-DOPA
Direct precursor to dopamine; supports neurotransmitter synthesis
L-Theanine
Calming amino acid from tea; increases alpha waves; sleep-friendly
Choline & Methylation-Relevant Molecules
Choline
Acetylcholine precursor; methyl donor; phospholipid synthesis for membranes
Microbial Metabolites (Postbiotic Layer)
Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
Acetate
Most abundant SCFA supporting gut barrier integrity and immune regulation
Butyrate
Key SCFA supporting mitochondrial function, gut barrier integrity, and neuroinflammation reduction
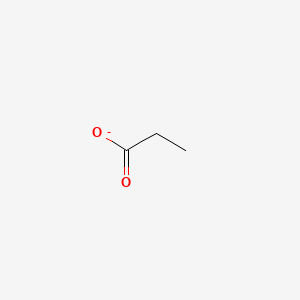
Propionate
SCFA supporting neuroinflammation reduction, blood-brain barrier protection, and neurotransmitter regulation
Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
Microbial metabolites supporting gut barrier, immune tone, and brain function
Secondary Plant Metabolite Conversions
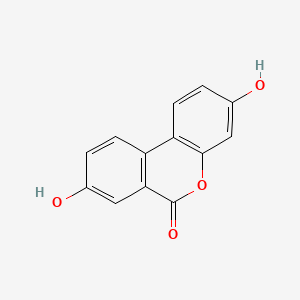
Urolithin A
Microbiome-derived metabolite from ellagitannins; supports mitochondrial resilience and mitophagy