Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids (ALA, DHA, EPA, DPA)
Overview
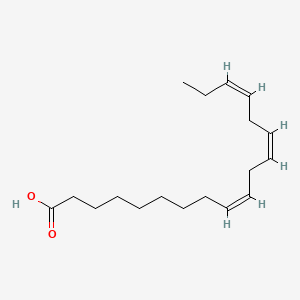
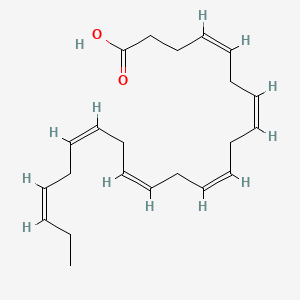
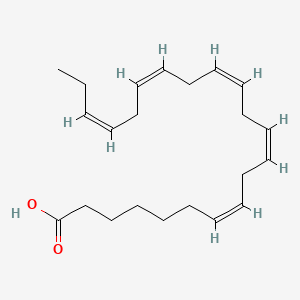
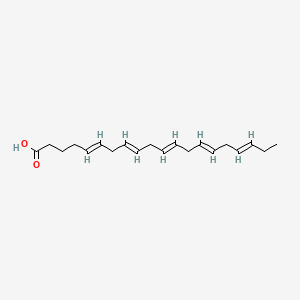
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are essential polyunsaturated fats that are central to the BRAIN Diet. DHA constitutes approximately 14% of brain polyunsaturated fatty acids and is critical for membrane fluidity, neurotransmitter receptor function, and synaptic plasticity. Omega-3s produce specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) including resolvins, protectins, and maresins, which actively terminate inflammation without suppressing immune function. They also support the endocannabinoid system through production of N-acyl ethanolamines, improve vagal tone and heart rate variability, and work synergistically with B vitamins in methylation processes. Phospholipid-bound forms (from krill oil, fish roe) cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than triglyceride forms.
Recipes
Foods
Biological Mechanisms and Implications
| Biological Target | Therapeutic Areas | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Inflammation & Oxidative Stress | Essential omega-3 precursor; limited conversion to DHA/EPA; contributes to omega-3 pool for anti-inflammatory effects |
References
- Lipids constitute 50–60% of brain dry weight; DHA ~14% of brain PUFA varies by region; omega-3s influence gene expression, neurotransmission, inflammation resolution, and synaptic plasticity McNamara and Carlson 2006
- Phospholipid-bound omega-3s (e.g., krill oil, fish roe) enhance brain DHA accretion via LPC transport; APOE4 carriers show reduced brain DHA uptake Arellanes et al. 2020
- DHA or EPA incorporated into PC and converted into lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) crosses the blood-brain barrier far more efficiently than free fatty acid or triglyceride-bound forms Patrick 2019
- Phospholipid-bound omega-3s such as krill oil and fish roe were 1.9-fold more efficacious for brain gray matter DHA accretion in porcine models Liu et al. 2014
- Specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs), derived from omega-3s (DHA and EPA), terminate inflammation without suppressing immune surveillance; include resolvins, protectins, and maresins Serhan and Petasis 2011
- SPMs modulate endothelial function through nitric oxide release and support neuroprotection by limiting glutamate-induced excitotoxicity Briones et al. 2025
- In a controlled endotoxemia model, high-dose EPA+DHA (3.6 g/day) attenuated fever and downstream cytokines, suggesting omega-3s reshape the resolution phase of acute inflammation Ferguson et al. 2014
- Phospholipid methylation (PLM), enhanced by dopamine D4 receptor activity, alters membrane structure, facilitating faster neuronal recovery and influencing ion channel behavior in gamma oscillations Martel et al. 2011
- Abnormalities in membrane composition and PLM have been linked to impaired ion channel regulation and reduced gamma-band activity in ADHD Wilson et al. 2012
- While folate is normally considered the primary nutrient for homocysteine reduction, long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin B12 also contribute meaningfully; B12+fish oil lowered plasma homocysteine by 39% Tao Huang et al. 2015
- B vitamin supplementation slowed cognitive decline only in participants with adequate omega-3 status, supporting a nutrient synergy model Oulhaj et al. 2016
- Western diets can skew n-6:n-3 ratio as high as 20:1, contributing to chronic inflammation and neurotransmitter dysregulation Simopoulos 2011
- Most research showing brain function improvements lean towards higher ratio of EPA to DHA (e.g., 2:1 ratio), with DHA having a more structural role and EPA with a more functional role Pei-Chen Chang 2021